Electronic Dosing Device (EDD)
The Electronic Dosing Device (EDD) effectively monitors and controls turbid stormwater runoff by sampling and dosing the optimal amount of C4E’s proprietary environmental treatment flocculants. These systems are designed to adjust the dosing proportionally to the flow of stormwater, utilizing gravity-driven movement. This approach results in high-quality water without the need for expensive filtration systems, significantly reducing operational costs. By optimizing the chemical dosing process, the EDD ensures compliance with environmental standards and helps maintain water quality at a fraction of the cost of traditional treatment methods.

How the Electronic Dosing Device (EDD) Works
- Automated Chemical Dispensing: The EDD uses electronic controls to dispense chemicals in precise quantities.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors continuously track chemical levels and dosing performance, allowing for real-time adjustments.
- Programmable Dosing Cycles: Users can set customized dosing schedules to meet the unique requirements of their system.
- Integration with Systems: The EDD integrates seamlessly into existing treatment setups, enhancing overall performance.
Key Feature the Electronic Dosing Device (EDD) Works
- Precision Delivery: Ensures exact chemical dosing, minimizing waste and overuse.
- User-Friendly Interface: Equipped with intuitive controls for easy setup and operation.
- Real-Time Data Logging: Captures and stores dosing information for performance analysis.
- Corrosion-Resistant Build: Constructed with durable materials to withstand harsh environments.
- Compatibility: Works with a wide range of chemicals and treatment systems.
Benefits of the Electronic Dosing Device (EDD)
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces excess chemical usage, saving money and resources.
- Environmental Responsibility: Minimizes chemical waste, supporting sustainability goals.
- Compliance Assurance: Helps meet regulatory requirements by ensuring precise chemical management.
- Process Optimization: Enhances system performance with reliable chemical dosing.
- Ease of Use: Simple installation and operation for seamless integration into various systems.
What the Electronic Dosing Device (EDD) Can be Use for
The EDD is suitable for use in:
- Water Treatment Systems: Ensures the optimal distribution of chemicals for chemical dosing in various water treatment systems, including municipal, industrial, and agricultural setups.
- Industrial Processes: Optimizes chemical use in manufacturing processes such as cooling water treatment, effluent treatment, and corrosion prevention.
- Energy and Process Optimization: Helps in optimizing chemical dosing for energy efficiency, reducing chemical consumption, and improving process efficiency.
- Wastewater Treatment: Supports controlled dosing of coagulants, flocculants, and other chemicals used in wastewater treatment plants.
- Desalination and Reverse Osmosis Systems: Provides consistent dosing for membrane cleaning and maintaining operational efficiency.
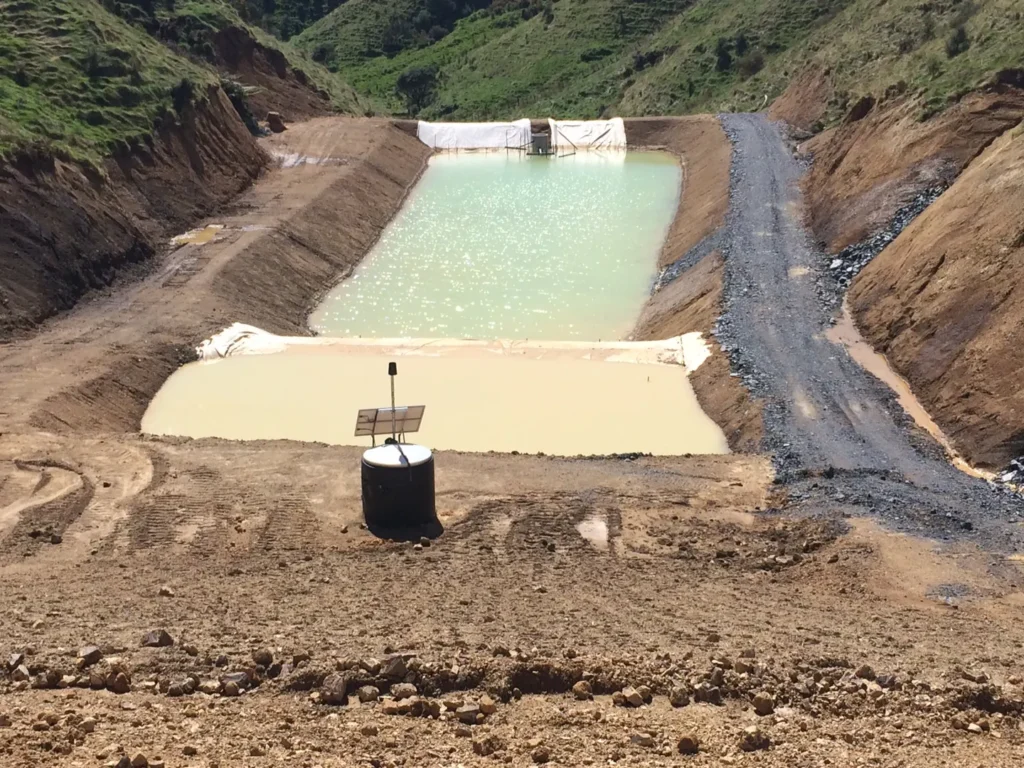

The Electronic Dosing Device (EDD) is a highly effective solution for optimizing chemical usage in various environmental and industrial applications. By offering precise dosing control, it reduces operational costs, ensures regulatory compliance, and enhances process efficiency. Whether it’s for water treatment, energy optimization, or waste management, the EDD provides a cost-effective, reliable, and environmentally-friendly alternative to traditional chemical dosing methods. The EDD’s flexibility and ease of integration make it ideal for companies focused on improving their sustainability practices while maintaining high levels of performance and cost-efficiency.
This system represents a significant step towards smarter, greener operations, providing a balance between environmental protection and economic viability.